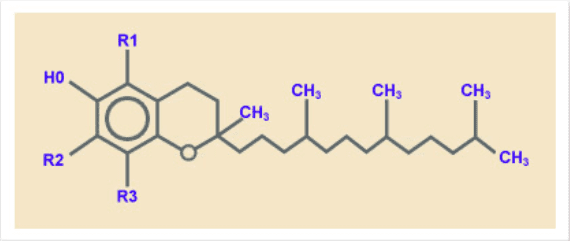
1. Vitamin E is actually a complex of 8 different compounds, which include 4 tocopherols and 4 tocotrienols , each of which can be further divided into alpha, beta, gamma, and delta forms. While tocopherols have been the focus of most research, tocotrienols have not received as much attention. Consequently, many vitamin E supplements available in the market predominantly feature tocopherols, leaving the full potential benefits of tocotrienols yet to be explored.

2.Many Vitamin E supplements on the market primarily contain tocopherol as their main ingredient, which means that their full benefits for the body are not realized. Recent research has shown that tocotrienols are powerful antioxidants with various health benefits. They possess neuroprotective properties, help reduce cholesterol levels, promote skin and hair growth, protect the liver, prevent strokes, and may even help prevent sterility. Additionally, tocotrienols are known to combat inflammation.

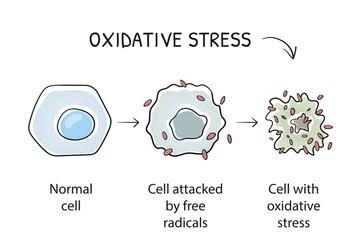
3.Actually, tocotrienols help significantly in the body to lower inflammation. Studies have shown that tocotrienols are five times more potent than tocopherols in reducing inflammation. Research has shown that tocotrienols are available in different forms: Delta tocotrienols and gamma tocotrienols, of which delta tocotrienols have five times more potency than tocopherols to fight inflammation in the body. In fact, tocotrienols are far more potent than tocopherols in the prevention of oxidative stress.

4. The widespread benefits of tocotrienols can be summed up as :
• Powerful antioxidant.
• Powerful antimicrobial
• Neuro-protective.
• Anti-cholesterol effect.
• Anti-tumour, anti-cancer,
• Prevents stroke
• Anti-inflammatory, prevents autoimmune diseases.
• Protective to the cardiovascular system, hepato-protective, and promotes hair growth.
• Promotes bone health, especially for menopausal women.

5. Extensive studies have been carried out on the neuroprotective role of tocotrienols, which have shown very positive results on people with stroke, nerve disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Studies have revealed that astrocytes play an important role in restoring neuronal cells and protect neurons against oxidative stress. Tocotrienols help in preventing glutamate-induced injury and prevent the death of astrocytes. Therefore, tocotrienols are crucial in minimizing neurodegenerative diseases and stroke.

6. There are several studies and clinical trials showing evidence of anti-inflammatory effects of tocotrienols by controlling the inflammatory mediators. Research suggested that tocotrienols block the activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB), one of the main regulators of inflammatory response. Supplementation of tocotrienols is found to reduce tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1 and phorbol ester. It is a potential agent with significant anti-inflammatory effects in atherosclerosis, thyroid diseases, and autoimmune diseases.

7. Research shows that tocotrienols are usually safe for healthy individuals at a minimum dosage. But they do have anti-coagulant properties, so people with blood disorders should avoid taking them. Some contraindications:
• Individuals allergic to any compound of Vitamin E should strictly avoid it.
• As mentioned already, people with bleeding disorders, or anyone who will undergo surgery, should avoid it as it may slow blood clotting.
• Tocotrienols may interact with medicines like anticoagulants and antiplatelets and increase the risk of bleeding.
• Overdosing should be avoided as it may cause physical symptoms like headache, fatigue and GI symptoms.
•High doses of tocopherol can interfere with the efficacy and absorption of tocotrienols.

8.Tocotrienols are generally safe when taken by mouth. There is no standard medical recommendation for dosage. However, under medical supervision, the typical dose of tocotrienols in adults is 100mg – 200mg per day. Dosage can vary depending on the specific health requirement. Supplements are mainly derived from palm and annatto derivatives. They are fat- soluble and best absorbed along with a meal.

9. Food sources: Generally, tocotrienols are rarely found in nature. Even if some food sources are available, they are available in very low quantities. Palm oil has the most concentrated and natural source of tocotrienols, but at a very low level, which is not sufficient for potential health benefits. Other food sources are annatto ,edible oils like rice bran oil, grape seed oil, castor oil, coconut oil, peanut oil, linseed oil, cod liver oil, hazelnuts, oats, olive oil, maize, wheat germ, nuts and barley. Fish like salmon, trout, fruit like avocado, mango, vegetables like red pepper, greens, turnip, and squash are rich in vitamin E and its compounds.

10. Takeaway is that tocotrienols are the least known compound of the Vitamin E family, yet they are the most potent antioxidant and have strong evidence of widespread health benefits. Newest studies show that this compound has senolytic properties, a strong immune response, and apoptosis. They can slow down the process of ageing, reduce oxidative stress, and lower malignant potential. Though in small quantities, regular intake of natural sources of tocotrienols is sufficient for a healthy individual. Supplementation is required when medically prescribed.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏