
Peace and love 🙏


Peace and love 🙏
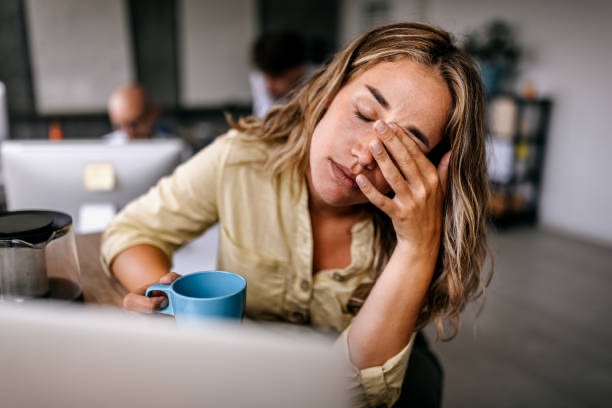
1.Cortisol is a stress hormone released from the adrenal glands, which is ideally secreted during a fight-or-flight response. However, in today’s world, our daily lives are filled with stressful situations, such as competition, comparisons, peer pressure at work, negative people, and relationships stress. As a result, cortisol is released not just in short bursts but remains chronically elevated. This persistent high level of cortisol keeps the body in a constant state of stress, leading to chronic inflammation, sleep problems, and various diseases.
2.Cortisol plays essential role in the body for survival. But when cortisol is elevated for a longer period of time can lead to health issues like weakened immunity, metabolic syndrome and mental health issues. The functions of cortisol are :
– Maintaining blood pressure
– Elevating blood sugar levels
– Regulating the circadian rhythm
– Facilitating the utilisation of energy from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats
– Reducing inflammation

3. Sleep-wake cycle follows a synchronised rhythm with the night and daytime. During the sleep phase, the body goes through different stages, such as:
• Non-REM stage: The phase where the body and mind, being awake, slowly move to a calmer state before falling asleep. Followed by a stage where the body’s core temperature drops, brain waves slow down. After this, a stage emerges where the heartbeat, breathing, and brainwaves slow down, entering a deep state of relaxation.
• REM state: This stage occurs normally after the deep sleep phase. In this phase, people have vivid dreams, and intense dreaming appears. There is weakened muscle activity similar to temporary paralysis. This stage is important as the brain is cleaning out the buildup of waste and toxins.

4. HPA axis: The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis is responsible for the neuroendocrine regulation. Hormones like melatonin and cortisol from the HPA axis modulate the sleep-wake cycle. When there is disruption of this axis disturb the sleep cycle. Studies show that there are reciprocal interactions between sleep regulation and the HPA axis. Stressful situations like PTSD, emotional trauma, and chronic workload can lead to long-standing sleep issues like insomnia, sleep deprivation, and lack of restorative sleep, which in turn lead to disruption of the HPA axis and vice versa.
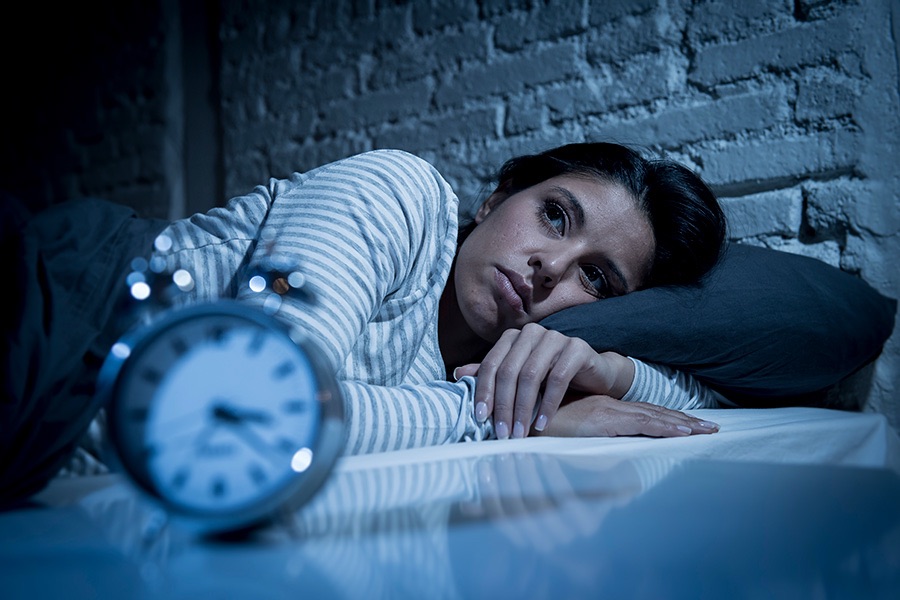

5. The HPA axis and sleep have a significant interconnection. Good quality sleep, deep sleep causes an inhibitory effect on the HPA axis, whereas hyperactivation of the HPA axis leads to overload of glucocorticoids, wakefulness, and loss of sleep. Sleep disorders related to HPA dysfunction are:
•Insomnia is a common sleep disorder which is found to have a connection with an increase in ACTH and consistent cortisol levels and arousal of the central nervous system.
•Obstructive sleep apnea or daytime sleepiness has been associated with elevated pro- inflammatory cytokines, IL-6 and TNF.
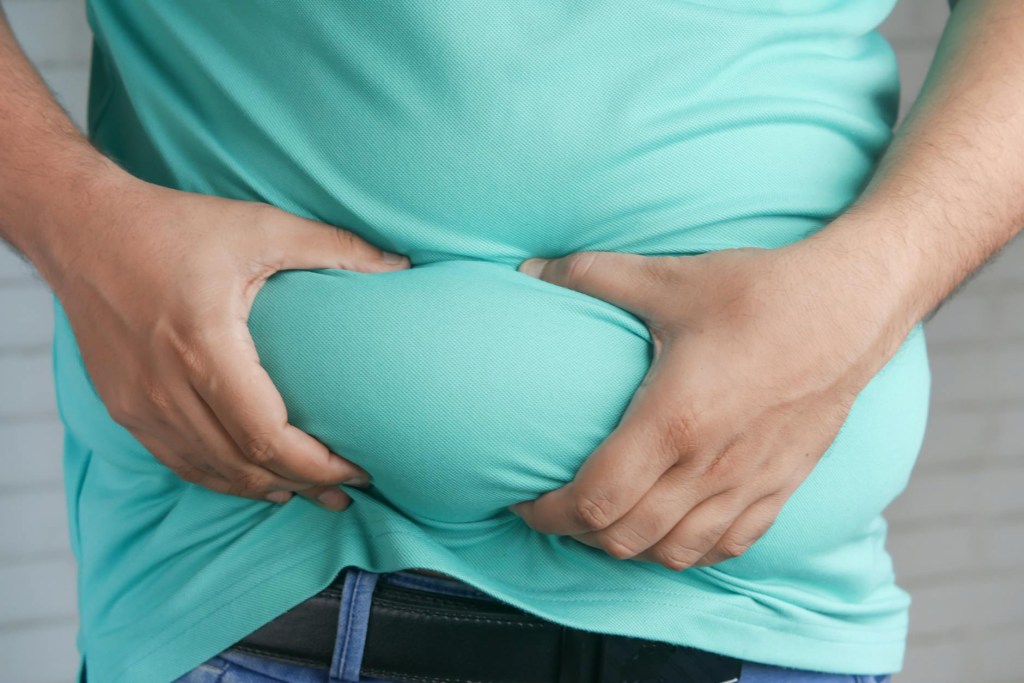

6. Elevated cortisol level: Studies show that sleep deprivation has a direct connection to elevated cortisol levels, long hours of wakefulness in the daytime, glucocorticoid overload, and disruption in the HPA axis. These directly affect the well-being of the individual and increase the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Other symptoms of elevated cortisol levels are:
• Weight gain
• High blood pressure
• Weakness of bones
• Muscle weakness

7. Cortisol level: Normally, there is a spike of cortisol level in the morning, known as the awakening response, and it continues for about 60 minutes thereafter. Then, gradually the level-starts dropping and reaches the lowest level towards the evening/midnight. The factors which can affect the cortisol levels are:
• Stress
• Disturbed routine sleep schedule
• Morning light may cause the surge
• Cushing’s syndrome

8. Stress and cortisol level: Cortisol is a steroid hormone which is released from the adrenal glands in the body’s response to stress. Cortisol also releases sugar from the liver to combat stress. In addition to this, sleep and stress are also closely linked. Prolonged stress can lead to sleep disorders like acute insomnia. The types of stress when cortisol is secreted are:
•Short-term stress
•Long-term stress
•Trauma, both psychological and physical.
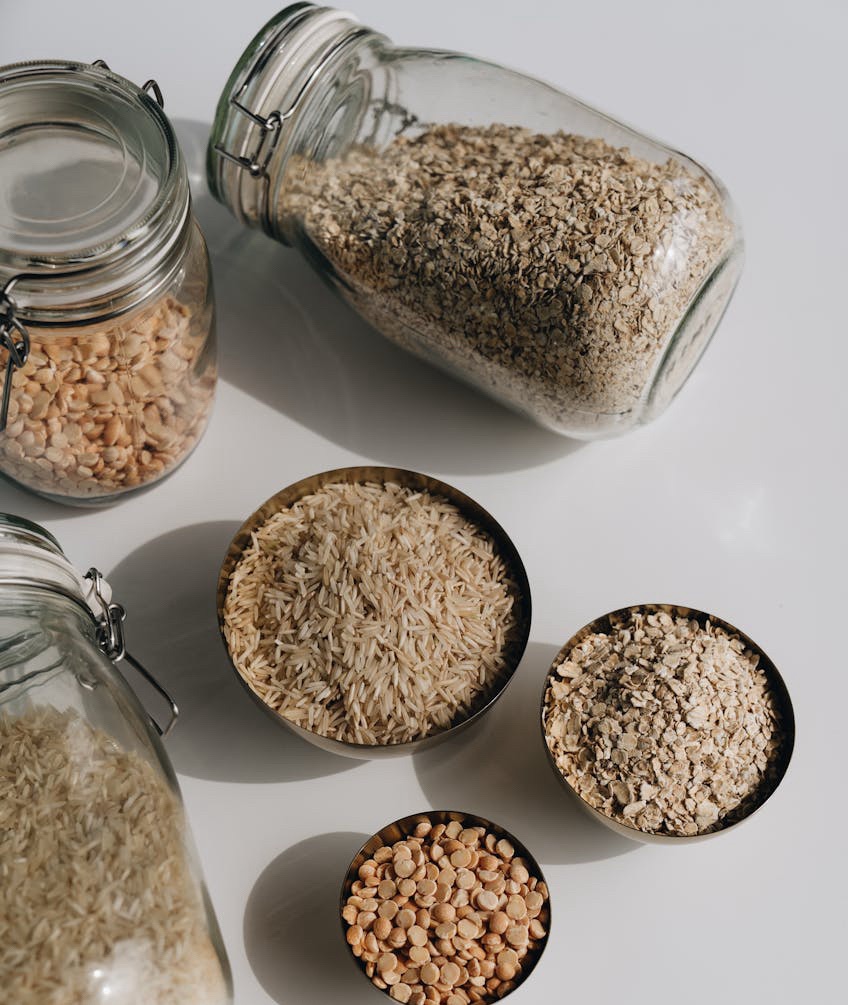


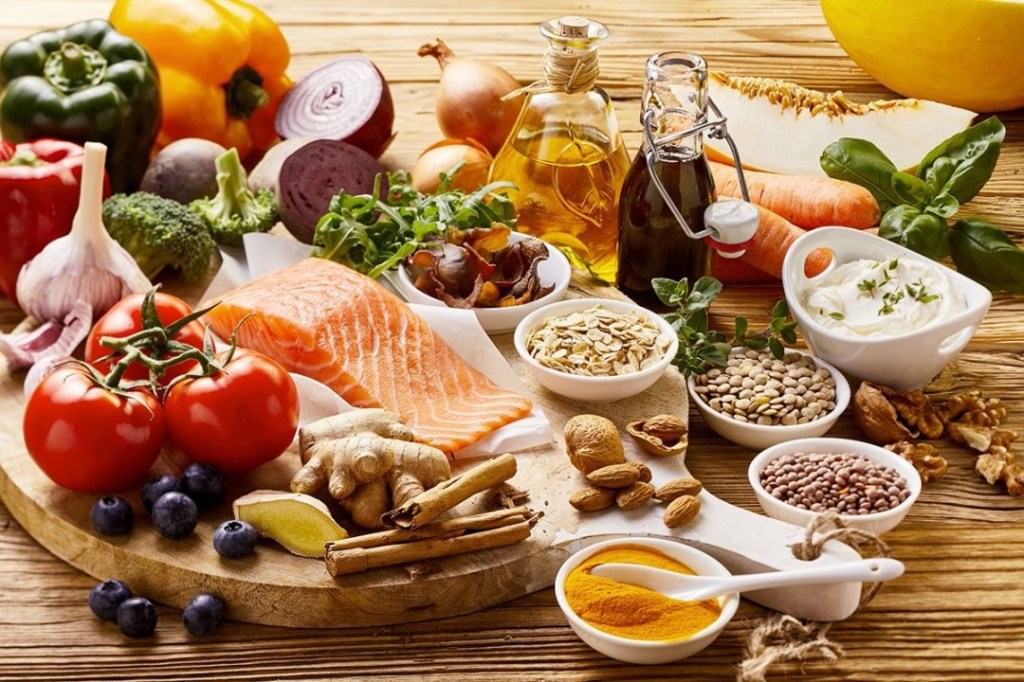
9. Food and cortisol: Certain foods can support gut health, reduce stress and lower the cortisol level naturally:
• Whole grains and natural fibres – Whole grains are rich in polyphenols, which can support gut health and reduce stress and cortisol. Fibrous foods like vegetables, fruits, and berries contain both polyphenols and antioxidants that help reduce cortisol levels.
• Dark chocolate (70 – 80%) – Flavonoids in dark chocolate can lower the stress response and cortisol from the adrenal glands.
• Green tea contains polyphenols, catechins, and L-theanine, which can lower stress reactivity.
• Probiotics/Prebiotics are linked to healthy gut health, reduce stress and cortisols.
• Healthy fats in nuts, fatty fish, and seeds rich in omega3-fatty acids reduce stress and support mental health.
• Water – Consuming water throughout the day prevents dehydration and controls the cortisol level.
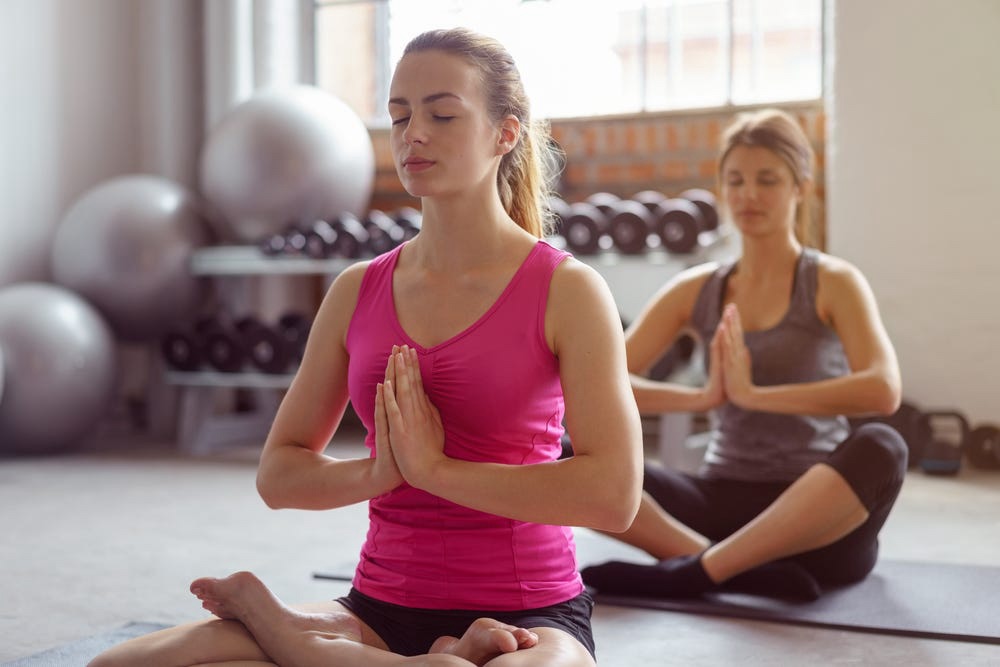


10. Natural habits that can keep the cortisol level under control:
• Good sleep routine – Firstly, keep away from cell phone or any kind of distraction at least 1 hour before bedtime, avoiding alcohol, caffeine intake and nicotine 5-6 hours before bedtime, maintain a bedtime schedule; going to bed and waking up the same time every day is important for sleep hygiene.
• Daily routine exercise, nature bathing, walking or any kind of physical activity.
• Practise deep breathing techniques like Pranayama, mindfulness breathing, Meditation, yoga, tai-chi.
• Maintaining your mental health by managing your personal relationships, staying away from negative people and a negative environment, cultivating hobbies, laughing, and listening to music.
• Spirituality – believing in spiritual faith, attending spiritual workshops, meditation, community spirit, kindness /charity /voluntary works, helps maintain cortisol levels.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏

Peace and love 🙏
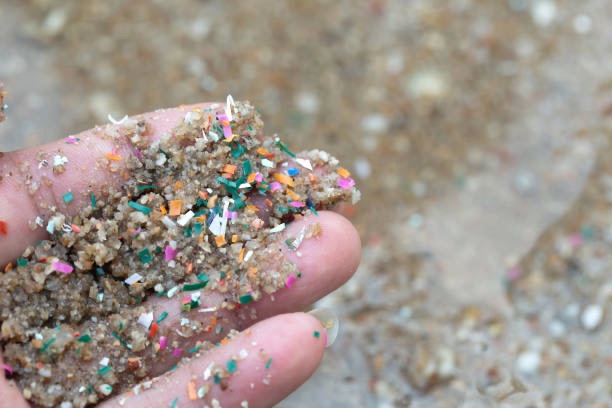

1. Microplastics are small plastic particles, less than 5mm in size, while nanoplastics are extremely small, less than 100 nanometers, and are found in the whole environment, everywhere, in the air, water, and soil. The greatest impact of these small particles on aquatic life has been a trending topic in recent times. The potential hazard to human lives is a great concern, too. Microplastics come from many sources. Tiny particles produced from polyethene plastic are used in many cosmetic products, even in health products, as an exfoliate. Plastic pollution is seen in both food and drink product packaging, the most hazardous being the bottled water. The direct effects of plastic particles, especially chemicals like BPA, on human health are still the subject of ongoing research widely carried out.
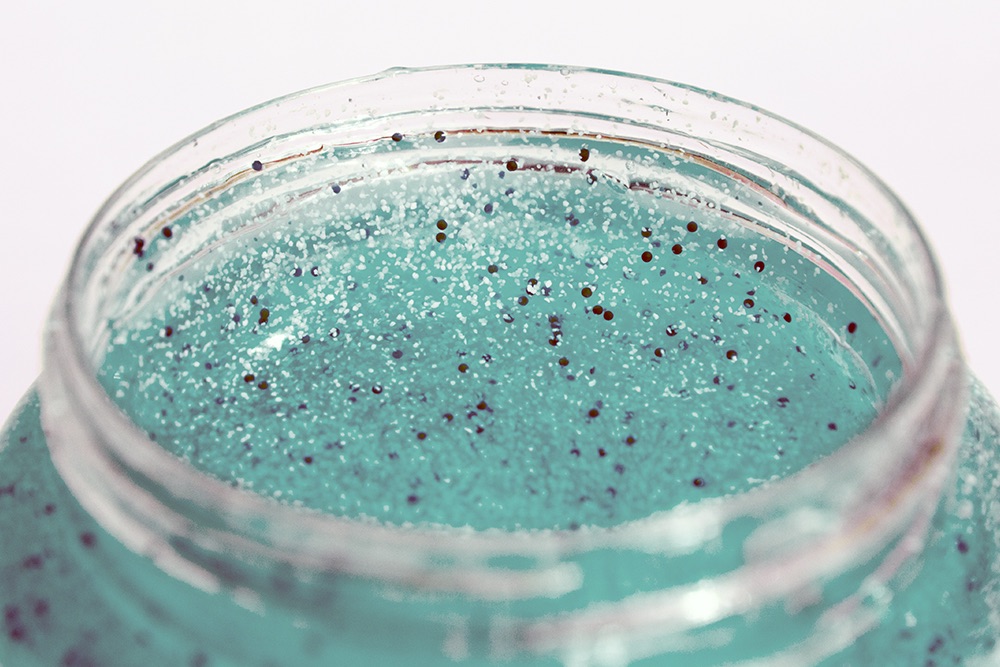


2. Microplastics have been used in many industrial and cosmetic products as microbeads. They are also used in toothpaste, as vectors for drug delivery, cleaning agents, plastic packaging in food and drinks, and manufacturing products. Some examples of primary and secondary uses of microplastics:
• Personal care /cosmetics like toothpaste, facial scrubs, and cleansers.
• Agricultural products are used as coatings in fertilisers and in seeds.
Industrial products such as paints, textiles, tyre materials, and many types of machinery.
• Sports like synthetic turf.
• Secondary microplastics are released from packaging and fragmentation of bottles, bags and debris, produced by fragmentation and weathering due to exposure to UV lights, weather and mechanical activity.

3. Microplastics as a global threat has become an issue of grave concern because of their impact on all compartments of the environment, that is, air, water and soil. The most common concern is the food packaging on major food items such as mineral water, drinks, dairy, snacks, meat, fish, and frozen products. The contact of contamination is between the food item and the container/ the outer package is actually the cause of mutual transfer between the content and the plastic. Besides these, microplastics are also found in sediments in freshwater, the ocean, soil ecosystems, and on beaches, becoming a threat to not just humans but also other life on earth, including aquatic animals.
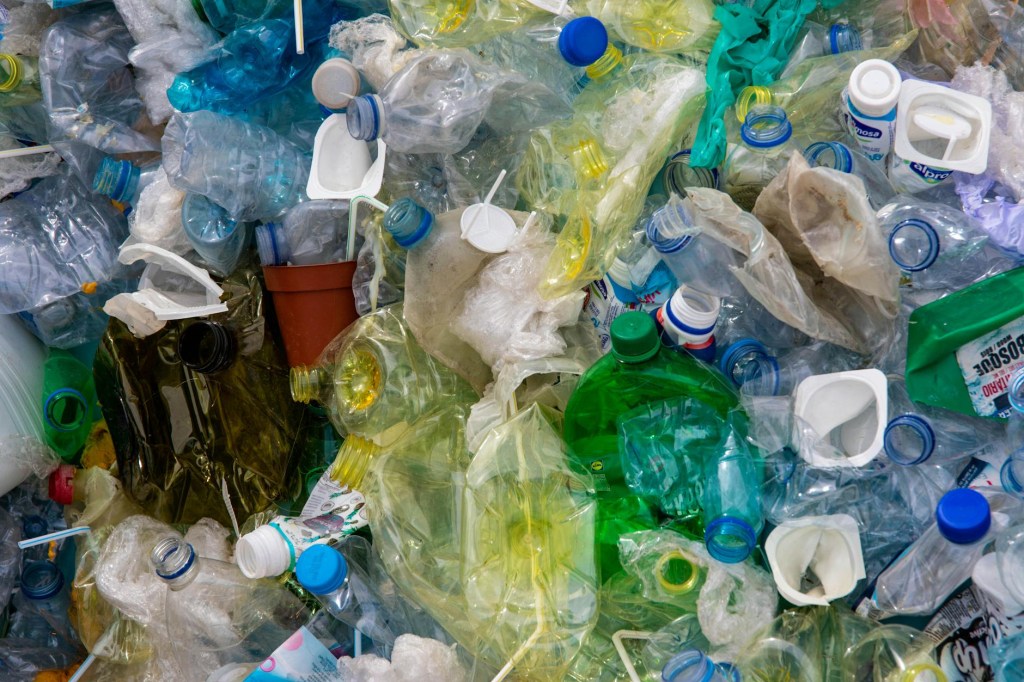

4. Microplastic pollution: Over the years, the growing presence of microplastics in the environment has increased day by day. The microplastics have high polymer content, so they remain non-perishable, non-degradable in soil, and insoluble in water. The direct impact on humans can be:
•Consumption of bottled water and plastic packaged drinks.
•Food packaging of different items.
•Indirect effect of microplastics from consuming aquatic foods like seafood, fish, and crustaceans.
•Personal care items like fabrics ( sportswear), toothpaste, face scrubs, and exfoliating products through micro beads.
•Industrial products.
5. Accumulation in the human body: Microplastics/ Nanoplastics easily accumulate in the human body through different sources :
• Ingestion through the food supply chain.
• Inhaled through air pollution.
• Ingested through drinks and water.
• Microplastics can enter the human body through dermal contact via sweat, wounds, an indirect route like unfiltered sewage plant, seawater, and seafood.
6. Recent studies have detected microplastics/nanoplastics in different human tissues and organs, including the brain. Traces are found in blood, liver, kidneys, lungs, and saliva. They mainly enter into different organs and tissues through the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Nanoplastics, which are even smaller ( less than 1micrometer ), are more dangerous as they can infiltrate the human cells. Microplastics have also been found in human breast milk, placenta, meconium, and an infant’s first stool.

7. Impact on human health:
•Oxidative damage: Microplastics can cause oxidative damage, DNA damage and changes ingene activity.
• Reproductive effects can be ovarian scarring, low sperm count, and metabolic disorders in offspring.
• Deposits of BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals can cause damage to the brain, nervous system, reproductive, gastrointestinal and respiratory systems.
• Other effects can be inflammation, cell death, changes in hormone and lipid metabolism, and an altered gut microbiome.
8. Research shows that potential health risks due to absorption, inhalation and ingestion of microplastics and nanoplastics are an alarming public health issue. The most important key effects can be:
• Regular or frequent exposures can cause chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal system, endocrine disruptions, and a weakened immune system.
• Accumulation in the respiratory system can cause lung inflammation, chronic asthma, chronic obstructive lung diseases and lowered lung function.
• The reproductive system can be affected, leading to low sperm count and infertility.
• Accumulation in organs like the liver, kidneys, spleen, and placenta can lead to scarring and functional irregularities.
• Increased risk of cancers and cardiovascular issues.


9. Supporting the body’s natural detoxification process can be useful in removing microplastics to some extent. Some of the proven ways by which microplastics can be removed from the body are:
• Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins.
• Sweating it out by physical exercise, running, or walking.
• Consumption of gut-healthy food like fermented food, prebiotics and probiotics.
• Antioxidant-rich foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, berries, and cruciferous vegetables.
• High fibre vegetables for forming bulk and binding the waste to be disposed of from the body.


10. The use of plastic is a global environmental hazard which has been taken seriously worldwide. Some important steps taken are:
• Minimal use of plastics in food supply chains and industrial uses.
• Use of plastic alternatives like bamboo, wood, seaweed, metal, and glass packaging.
• Replacing household items like/with silicon food bags, ceramic, glass utensils, stainless steel containers, wooden utensils.
• Using reusable materials derived from sugarcane, wheat, seaweed, packaging materials like cardboard, paper, plant-based wraps, and foams.
• Natural fibres like jute, organic cotton, and wool.
• Extensive research for the environmental clean-up of plastics and recycling plastics is ongoing in many countries. Plastic-eating bacteria (Ideonella sakaiensis), microbes like Pseudomonas, and Bacillus have been identified which have biodegradable capacity to break down plastics.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏

Peace and love 🙏

1. Poor gut health means poor metabolism, microbiome irregularities, digestive issues, chronic inflammation, built-up toxins, elevation of cortisol and hormonal issues. Therefore, a weak gut health profoundly affects the endocrine ecosystem. On the other hand, studies have confirmed that gut microbiota can be influenced by the hormonal environment. Some studies suggest that there is a connection between gut microbiome and sex-related diseases like polycystic ovarian disease, post-menopausal osteoporosis, ovarian cancer and type-1 diabetes.

2. The gut microbiome normally maintains and regulates digestion, nutrient absorption, immune protection and hormonal regulation. In fact, a balanced gut microbiome is the key element in stabilizing hormones like oestrogen, cortisol, and insulin. When the gut microbiome and its ecosystem are in balance :
• Digestion is smooth
• Hormones are regulated
• Inflammation is low
• Mood and energy are improved
• The estrogen level is stable

3. Trouble arises when the gut microbiome goes out of balance and gut health is disturbed; the hormonal health is impacted as well. The common issues may appear:
• Body weight may fluctuate
• Estrogen levels may shoot up
• Other hormone levels may fluctuate rapidly
• Sugar cravings increase
• Toxin levels may rise
• Hair fall
• Irregular periods
• Trouble sleeping
4. The gut microbiome and oestrogen link: A special group of gut microbiome named estrobolome maintains and regulates the oestrogen cycle in the body. The bacterium helps to clear out the excess oestrogen from the body and maintain the menstrual cycle:
When estrobolome functions properly,
• Menstrual cycle remains regular
• The oestrogen level is regulated
• PMS remain under control
• Acne and skin issues are absent
• Bloating and gas issues are nil
When estrobolome is unhealthy,
• Estrogen levels imbalances
• Instead of clearing, the oestrogen recirculates in the body
• Acne, bloating, and gas issues may arise

5. When gut health is optimised, the estrobolome produces enzymes like betaglucoronides which not only metabolise and maintain the optimal levels of oestrogen, but also help in breaking complex carbohydrates, absorption of bilirubins and flavonoids. Oestrogens are basically produced by the female ovaries and adrenal glands. In women, the hormone plays an important role in reproductive functions, regulating body fat, maintaining heart health, bone health and brain health. In men, this hormone helps to maintain libido and the maturation of sperm.

6. PCOS linked to gut health: Many women who suffer from PCOS usually have gut health issues, including slower metabolism and chronic inflammation. Other issues which are commonly seen are:
• Blaoting, gas issues
• Irregular digestion
• Sugar cravings• High insulin levels
• Depressions, mood swings
• Low energy
• Irregular periods
• Skin issues, acne


7. Holistic health approach: To maintain stability and balance between gut health and hormonal balance, changing lifestyle habits, nutritional habits, and daily physical activity are the major steps towards this goal. Developing routine habits includes:
• Changing nutritional habits to whole foods.
• Timely eating habits
• Manage routine stress
• Mindfullness
• Breathing techniques like Pranayama
• Regular physical activity
• Maintaining a sleep routine
• Avoid the intake of unnecessary antibiotics
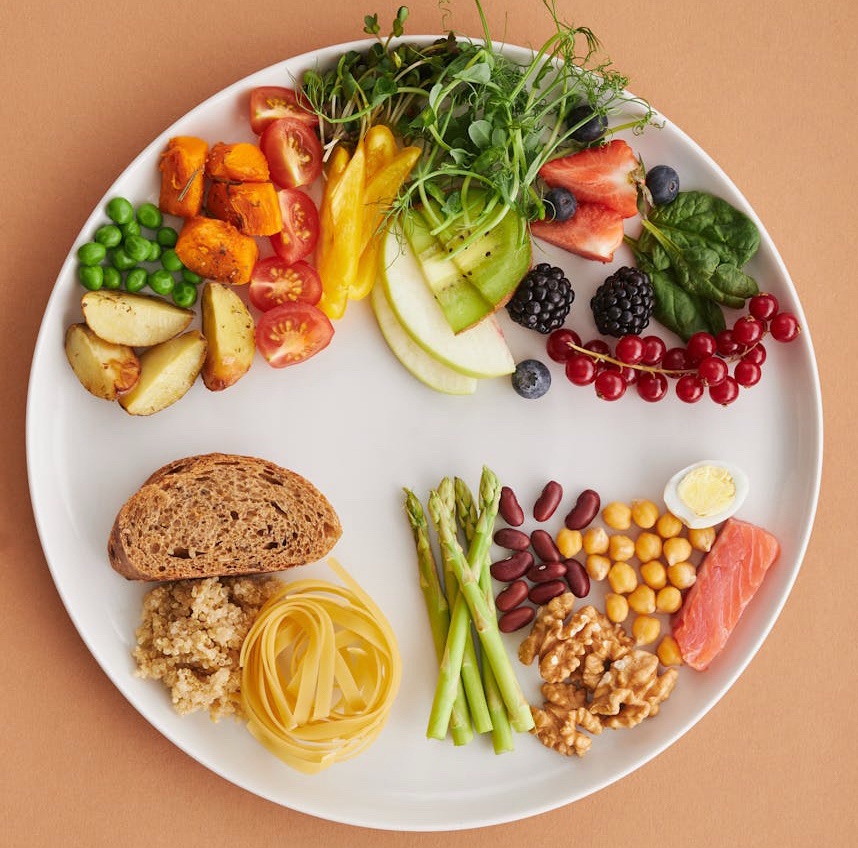

8. Nutrition plays a significant role in shaping gut health and maintaining hormonal stability. The important steps are:
• Completely avoiding processed, junk, refined and sugary foods
• Maintaining hydration, drinking plenty of water
• Focus on whole grains, lentils, beans
• High-fibre vegetables
• Fermented foods
• Omega-3 rich foods
• Herbal teas
• Fresh fruits

9. Probiotics/Prebiotics: Both probiotic and prebiotic foods strengthen gut health and support hormonal health. When consumed routinely, it significantly impacts digestion, slows down inflammation, improves sleep, and helps in managing PMS and PCOS in women.
•Probiotics like fermented food, such as pickled vegetables, kombucha, kefir and curds.
•Prebiotics include whole grains, onions, garlic, and bananas.

10. The major takeaways in optimising gut health and maintaining hormonal balance are:
• Always be careful what you put into your body. Food not only curbs our hunger but they feed our cells.
• Routine exercise helps in the detoxification of the liver and reduces daily cortisol levels, regulate the levels of sex hormones. Activities like Yoga, mindfulness practises, and breathing exercises maintain an optimal environment for the balance of the gut-hormone axis.
• Curbing smoking and limiting alcohol can prevent toxins from building up, supporting the liver in the detoxification process, which is crucial for endocrine health.
• Avoiding unnecessary antibiotics as they can disturb the ecology of the gut microbiome and disrupt its functions.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏


1. Self-awareness is quite a commonly used term for mental health and well-being. While it has been discussed frequently, many people lack its actual understanding. Our everyday life is often caught up in autopilot mode, so our quality of awareness is very low. Our thoughts, emotions, reactions, habits, routines and impulses of day-to-day life are all on autopilot, so that instead of being aware of them, they keep us in control every day. So, it is important to understand Self- awareness and learn this ability of self-observation to improve our quality of awareness.
2. Many times in real life, we have gone through similar experiences, similar kinds of failures, attract similar people, have similar reactions, similar impulses, similar emotional meltdowns; the reason is not the outside world, but it is our inability to understand ourselves and our unwillingness to change. Most of the time, we are not self-aware of our emotional state, lack understanding of our strengths and weaknesses, so we end up in similar situations and experiences. As an individual, it is important to learn self-assessment, introspection and the ability to recognise our thoughts, feelings, emotions and actions.

3. Self-awareness is a psychological skill of knowledge and understanding about one’s own emotional state. It’s about self-observation, self-assessment of one’s emotions, thoughts, feelings, reactions and actions. It’s a capability of recognising one’s own reactions, actions, and behaviour in interacting with the outside environment and other people. Self-awareness helps in identifying tendencies, understanding emotional states, strengths, weaknesses, limitations and personal goals. It’s a lifelong learning ability to develop confidence and optimism in this dynamic world.

4. Self-awareness can be beneficial in several ways:
• Helps in building self-esteem, self-control, creativity, and skills
• Benefits include self-acceptance, emotional growth, and self-development.
• Aids in decision-making.
• Understanding strengths, weaknesses, and limitations.
• Accurate self-reports.
5. For several decades, thousands of research studies have been carried out to understand the interconnectedness between self-awareness and important key attitudes of human behaviour like habits, feelings, emotions, happiness, stress parameters, empathy and job satisfaction. Broadly, two types of self-awareness studies are recorded as :
• Internal self-awareness: It’s the ability to observe and monitor our inner world, while some label it as a state of self-consciousness temporarily. It is found to be associated more with relationships and job satisfaction as we try to fit ourselves with our personal control and social control.
• External self-awareness: Some state it as the difference between how we see ourselves and how others perceive us. Studies show that people who understand how others see them can be more empathetic and understanding of others’ perspectives.

6. Extensive research has identified five layers of self-awareness:
• Physical: Awareness of your physical body as shape, size, gender, race, ethnicity and five senses.
• Energetic: The breath and energy levels, which include the life forces that help you to move, think, create and take action.
• Mental: The thoughts, feelings, emotions that help you to react and take actions for yourself, others and life.
• The Witness: When you learn to become your witness and become aware of the different layers of self-awareness without being judgmental. This is an essential part of the path of learning self- awareness because you can bring about changes, a better understanding of your flaws, unhelpful patterns of beliefs, and habits that need to change.
• Bliss: Deep connection with a Higher Self, the Truth. A spiritual interconnectedness with the Divine.

7. The skill of knowing yourself is the biggest deal. If we actively start employing this art of self- awareness, we see ourselves as in a mirror, no hidden veil, just inside out, the reality as it is. Then,we start to find acceptance within ourselves, develop resilience if changes are not possible, and consciously bring about changes in our reactions, habits, behaviour and actions in our day-to-day life whenever required. This makes our everyday life approach easier, better handling relationships with people around, self -efficacy in controlling our mind, emotions, impulses, feelings, reactions, dealing with the external environment, people and the world around as it is.

8. Being in a path of self-awareness asks us to understand:
• Clear knowledge of our basic nature, character, impulses, flaws and desires.
• Observe our own habits and behaviour in dealing with our inner world and external world.
• In alignment with our energy levels and breath, and how they are affected by our choices and lifestyle.
• Keep an eye on our thoughts, feelings, emotions, impulses and learn to respond rather than react to whatever life throws us.
• Being a witness to self (intuitive wisdom) so that self-acceptance is easier without being judgmental.
• Searching for our connectedness to something bigger than ourselves.

9. Practising and learning to seek self-awareness is far from being an easy task; it is a lifelong process. Our day-to-day life is so much attuned to working, earning money, parenting, paying the mortgage, bills, and routine hustles that we hardly get time for ourselves. Besides, many obstacles cause hindrance in this path :
• Fear – Knowing and understanding our vulnerability, uncomfortable emotions, and weaknesses.
• Attachment – attachment to people, desires, things can often lead to internal conflicts.
• Aversions – Conscious understanding and resurfacing of situations, people, we usually avoid, internal conflicts, unresolved emotions and discomforts.
• Ego- Instead of being the centre of the world around us, knowing that ego is that tool to distinguish us “I” from the outside world, learning to balance it with wisdom rather than controlling us.
• Ignorance – Learning and understanding about the larger picture of life, rather than being happy when life goes well and disliking it whenever life throws challenges.

10. Developing and seeking self-awareness is an ongoing process, a lifelong learning. In this process, as an individual, there is tremendous personal growth, control over emotions, decision- making and self-acceptance with limitations. Some of the basic strategies are:
• Daily practising mindfulness, calmness, and reflections upon thoughts without judgement.
• Journaling your thoughts, feelings, emotions, impulses on experiences and situations.
• Getting honest feedback from trusted friends, family members, siblings, and partners.
• Self-analysing the situations that can trigger strong emotional responses like anger, panic- attacks, pain, and fear.
• Self- assessment of limitations, weaknesses, strengths, and levels of resilience.
• Routinely reviewing the day-to-day reactions, actions, decisions and interactions.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏
1. Right from the biology textbooks in school, to higher levels of studies and research, the importance of mitochondria has been highlighted time and again. As previously mentioned, mitochondria are known as the ‘powerhouse’ of cells. They are the centre of energy production, metabolism, crucial for cellular functions, ranging from cellular activities, regulating vital functions and including cellular death. In other words, they are critical in maintaining overall health, preventing various diseases and increasing longevity.

2. Mitochondria have their own DNA and undergo a constant process of damage, repair, replacement, and distribution within cells of the body. Through mitochondrial dynamics, a damaged component or an impaired mitochondrion can be replaced, mitochondrial quality can be controlled, and mitochondrial functions can be maintained, thereby preventing disease processes and promoting overall health and well-being. So, continuous mitochondrial dynamics play a pivotal role in maintaining good health on the cellular level and overall longevity.
3. Mitochondria are an integral component of a cell that carries out a series of functions like cellular metabolism, energy production, fission, fusion, mitophagy, ion homeostasis, senescence and cell death (apoptosis). Studies have shown that mitochondrial dynamics play a pivotal role in diverse cellular functions, influencing the activation and functioning of cells and cell movement. Cell movement is the basis of vital processes like wound healing, tissue growth, the immune defence mechanism and disease-related processes like malignant metastasis. Therefore, mitochondrial health and functioning are fundamental to the body’s overall health at the cellular level.

4. Mitochondrial health impacts most of the vital systems of the body, including the immune system, bones, muscles, heart, neurological, cognitive and gut health. So, when mitochondria are dysfunctional or underperforming, the body will exhibit various symptoms like :
• Low immunity status.
• Metabolic syndrome
• Brain and cognitive disorder
• Fatigue syndrome
• Bone and muscle conditions like osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
• Inflammatory diseases.
• Chronic body pain.

5. Mitochondrial disorders are of two types: Inherited types and acquired types. Inherited Mitochondrial disorders can be caused by genetic mutations due to defective genes encoding the ETC (Electron Transport Chain) protein.
• Barth syndrome.
• Kearns- Sayre syndrome.
• Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia.
• Leigh syndrome.
• Ataxia.
Acquired types: Mitochondrial disease from external factors like toxins, drugs (mitotoxins), ageing, infections, inflammatory responses, secondary causes like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, long-standing COVID.

6. Symptoms of mitochondrial disorders depend on the underlying factors, such as:
•Inherited types usually affect multiple organs, such as the brain, heart, liver, and muscles.
•People may have muscle fatigue, cognitive decline, hearing loss, vision loss, and GI issues.
•Secondary types can be the consequence of the primary causes, like type 1 diabetes, cancer, mental health disorders, and heart diseases.
•Environmental factors like toxins and drugs may result in mitochondrial dysfunctions.
Acquired types may have both the symptoms of inherited types and the underlying primary cause.

7. Diagnosis and treatment depend mainly on the underlying factors, triggering causes and the primary disease. The diagnosis relies mainly on many criteria, such as clinical, biochemical, tissue, and molecular specificity of clinical and laboratory findings.Treatment depends on the family history, clinical findings, laboratory findings, and metabolic/ molecular diagnosis. Treatments are usually antioxidant intakes, regular calorie intake, exercise, and specific treatment depending on the primary disease and definite mitochondrial dysfunction.

8. Commonly used agents for the treatment of both inherited and acquired types are:
• Electron transport chain support, like CoQ10 (ubiquinol)
• Electron carrier support, such as Niacin and Riboflavin.
• Fatty acid oxidation support, Biotin L-carnitine.
• Enzyme co-factors like Thiamine, Pantothenic acid, Biotin, and Alpha-lipoic acid.
• Anti-oxidants like Vitamin E, C, L-carnitine, and CoQ10.

9. Mitochondrial diseases have no cure, but a holistic lifestyle approach can improve the quality of life. The focus is mainly on energy preservation, nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
• Conservation of energy is essential to reduce fatigue, like planning out the daily and weekly schedule, taking rest in between normal chores, using assistive devices to minimise effort, and seeking help to reduce workload.
• Balanced diet of healthy protein, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Hydration and using supplements for health support.
• Exercise may include moderate activity, such as walking, swimming, or aerobic exercise.
• Prioritising sleep, avoiding toxins like quitting alcohol and smoking, managing stress like meditation, mindfulness tools, and nature bathing.


10. In a nutshell, mitochondrial dysfunction is very complex in nature and still not completely understood. Mitochondrial dysfunction is differentiated as primary and secondary (acquired) types, and the diagnosis is again very complex. But there is the MDC scoring system, which is beneficial. Millions of people across the world suffer from some types of mitochondrial dysfunctions, which include diabetes, autism, cancer, blindness, heart, kidneys, liver or infertility issues, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and chronic fatigue syndrome. Bringing out lifestyle changes can be helpful to improve the quality of life as well as mitochondrial health.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏

So grateful as 2026 is approaching ! Here’s a New Year for fresh start, new opportunities and abundant hope to build our dreams. A new chapter of growth, self discovery and unforgettable experiences and memories to celebrate.
Here’s wishing to all my lovely bloggers, a year filled with great opportunities, endless happiness, great health and beautiful moments to cherish. Have a wonderful and blessed New Year 2026 !
Peace and blessings 🙏

Peace and love 🙏