1. Right from the biology textbooks in school, to higher levels of studies and research, the importance of mitochondria has been highlighted time and again. As previously mentioned, mitochondria are known as the ‘powerhouse’ of cells. They are the centre of energy production, metabolism, crucial for cellular functions, ranging from cellular activities, regulating vital functions and including cellular death. In other words, they are critical in maintaining overall health, preventing various diseases and increasing longevity.

2. Mitochondria have their own DNA and undergo a constant process of damage, repair, replacement, and distribution within cells of the body. Through mitochondrial dynamics, a damaged component or an impaired mitochondrion can be replaced, mitochondrial quality can be controlled, and mitochondrial functions can be maintained, thereby preventing disease processes and promoting overall health and well-being. So, continuous mitochondrial dynamics play a pivotal role in maintaining good health on the cellular level and overall longevity.
3. Mitochondria are an integral component of a cell that carries out a series of functions like cellular metabolism, energy production, fission, fusion, mitophagy, ion homeostasis, senescence and cell death (apoptosis). Studies have shown that mitochondrial dynamics play a pivotal role in diverse cellular functions, influencing the activation and functioning of cells and cell movement. Cell movement is the basis of vital processes like wound healing, tissue growth, the immune defence mechanism and disease-related processes like malignant metastasis. Therefore, mitochondrial health and functioning are fundamental to the body’s overall health at the cellular level.

4. Mitochondrial health impacts most of the vital systems of the body, including the immune system, bones, muscles, heart, neurological, cognitive and gut health. So, when mitochondria are dysfunctional or underperforming, the body will exhibit various symptoms like :
• Low immunity status.
• Metabolic syndrome
• Brain and cognitive disorder
• Fatigue syndrome
• Bone and muscle conditions like osteoporosis and sarcopenia.
• Inflammatory diseases.
• Chronic body pain.

5. Mitochondrial disorders are of two types: Inherited types and acquired types. Inherited Mitochondrial disorders can be caused by genetic mutations due to defective genes encoding the ETC (Electron Transport Chain) protein.
• Barth syndrome.
• Kearns- Sayre syndrome.
• Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia.
• Leigh syndrome.
• Ataxia.
Acquired types: Mitochondrial disease from external factors like toxins, drugs (mitotoxins), ageing, infections, inflammatory responses, secondary causes like cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, Parkinson’s disease, long-standing COVID.

6. Symptoms of mitochondrial disorders depend on the underlying factors, such as:
•Inherited types usually affect multiple organs, such as the brain, heart, liver, and muscles.
•People may have muscle fatigue, cognitive decline, hearing loss, vision loss, and GI issues.
•Secondary types can be the consequence of the primary causes, like type 1 diabetes, cancer, mental health disorders, and heart diseases.
•Environmental factors like toxins and drugs may result in mitochondrial dysfunctions.
Acquired types may have both the symptoms of inherited types and the underlying primary cause.

7. Diagnosis and treatment depend mainly on the underlying factors, triggering causes and the primary disease. The diagnosis relies mainly on many criteria, such as clinical, biochemical, tissue, and molecular specificity of clinical and laboratory findings.Treatment depends on the family history, clinical findings, laboratory findings, and metabolic/ molecular diagnosis. Treatments are usually antioxidant intakes, regular calorie intake, exercise, and specific treatment depending on the primary disease and definite mitochondrial dysfunction.

8. Commonly used agents for the treatment of both inherited and acquired types are:
• Electron transport chain support, like CoQ10 (ubiquinol)
• Electron carrier support, such as Niacin and Riboflavin.
• Fatty acid oxidation support, Biotin L-carnitine.
• Enzyme co-factors like Thiamine, Pantothenic acid, Biotin, and Alpha-lipoic acid.
• Anti-oxidants like Vitamin E, C, L-carnitine, and CoQ10.

9. Mitochondrial diseases have no cure, but a holistic lifestyle approach can improve the quality of life. The focus is mainly on energy preservation, nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
• Conservation of energy is essential to reduce fatigue, like planning out the daily and weekly schedule, taking rest in between normal chores, using assistive devices to minimise effort, and seeking help to reduce workload.
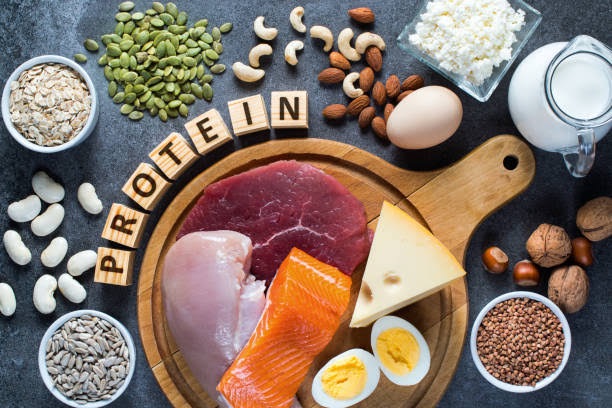
• Balanced diet of healthy protein, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Hydration and using supplements for health support.
• Exercise may include moderate activity, such as walking, swimming, or aerobic exercise.
• Prioritising sleep, avoiding toxins like quitting alcohol and smoking, managing stress like meditation, mindfulness tools, and nature bathing.


10. In a nutshell, mitochondrial dysfunction is very complex in nature and still not completely understood. Mitochondrial dysfunction is differentiated as primary and secondary (acquired) types, and the diagnosis is again very complex. But there is the MDC scoring system, which is beneficial. Millions of people across the world suffer from some types of mitochondrial dysfunctions, which include diabetes, autism, cancer, blindness, heart, kidneys, liver or infertility issues, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and chronic fatigue syndrome. Bringing out lifestyle changes can be helpful to improve the quality of life as well as mitochondrial health.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏










