1. Resistance starch is a new buzzword nowadays. But what exactly is resistance starch? Starches are a major portion of our everyday diet. They are usually found in grains, legumes, potatoes, and many other foods. Unlike simple starches, resistance starch passes through the digestive tract, the stomach and the small intestine undigested, and reaches the colon, where it is fermented by gut bacteria, like soluble fibres. Therefore, they are very gut-friendly, hence are potentially beneficial to health.

2. Several studies have identified the components of starches in different types of food, which are resistant to digestion, and can be very beneficial in the prevention and control of chronic diseases. Evidence has shown that starches present in food, which are rapidly digested, have significantly contributed to the growing risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, obesity, and colon cancer. Ongoing studies have shown that resistance starches are highly resistant to digestion by digestive enzymes like amylase in the small intestine and pass through the colon, where they are fermented by the microbiota.
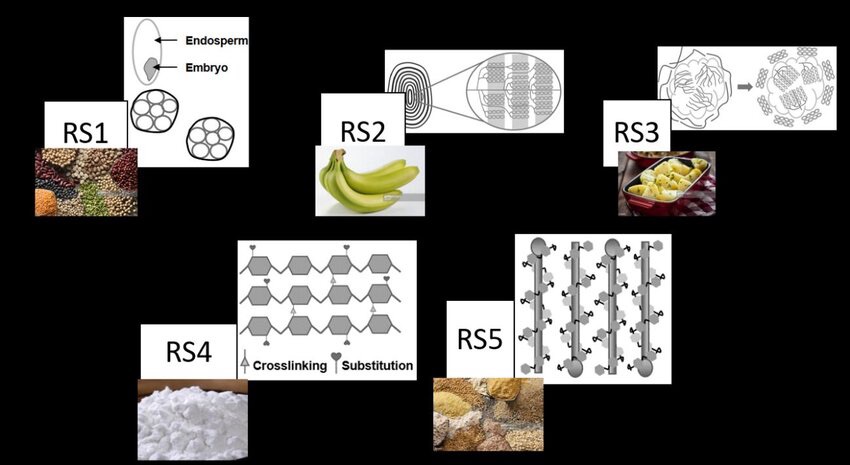
3. Five types of resistance starches have been identified such as :
• Type1 : Physically inaccessible starches like whole grains, coarsely grounded grains.
• Type 2: Granular starch like raw potato, raw banana starch.
• Type 3: Retrograde starch like cooked and cooled starch.
• Type 4: Chemically modified starch.
• Type 5: Amylose lipid complex.

4. Carbohydrates are simple in structure, like white rice, white bread, cakes, or refined food items. Resistance starches are complex carbohydrates which pass through the stomach and small intestine undigested and move to the large intestine to be fermented by the gut-friendly bacteria. Some examples of resistance starches are: Brown rice, whole grains, quinoa, lentils, plantains, oats and potatoes.
5. Simple starches are digested by the stomach enzymes and are responsible for spiking blood sugar and worsening insulin sensitivity. While resistance starches cannot be digested by the stomach enzymes, they travel through the small intestine and reach the colon. In the colon, they are fermented by the microbes and produce short-chain fatty acids like Butyrate. Butyrate improves insulin sensitivity, lowers inflammation, and provides food for gut-friendly bacteria.

6. Starch Retrogradation: It is a process where gelatinised starch molecules crystallize and become resistant to digestion in the stomach and small intestine. This trick can be done by cooling the simple starches after cooking and storing them in the refrigerator. Just before eating, heat them so that the content of resistance starch can be increased. Therefore, the effect of cooling the cooked rice or potatoes, bread can decrease the post-prandial glucose and insulin spike.

7. Simple ways to have resistance starches or increase the resistance starches content are:
• Cooking the rice, potatoes or pasta, and cooling them.
• Freeze and store them in the refrigerator.
• Reheating them before consuming.

8.Pairing food like carbohydrates with protein and fat can help in controlling the glucose spike and improving insulin sensitivity. Pairing potatoes with butter or olive oil, or rice with lentils or beans, is a common example. Acidifying the meal by adding lemon, vinegar, or fermented food can lower the rate of starch breakdown.

9. Again, food orders are another important trick to improve insulin sensitivity and lower the glucose spike. Instead of having carbohydrate first, it is wiser to eat the protein like eggs, meat or fish first, followed by vegetables and lastly the carbohydrate portion. This way, it will slow down the glucose digestion. Such behavioural change while following the food order either at home or in a restaurant can help to improve the metabolic response.

10. Eating a meal and then immediately sitting down to work, using the laptop, or taking a nap can negatively impact your metabolic response. Instead, after finishing your meal, consider taking a light walk or engaging in a gentle activity like cleaning or washing dishes. These activities can stimulate your calf muscles, particularly the soleus muscle, which can quickly utilise a significant amount of glucose. By sustaining contractions, this muscle helps burn glucose, contributing to better blood sugar control.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏