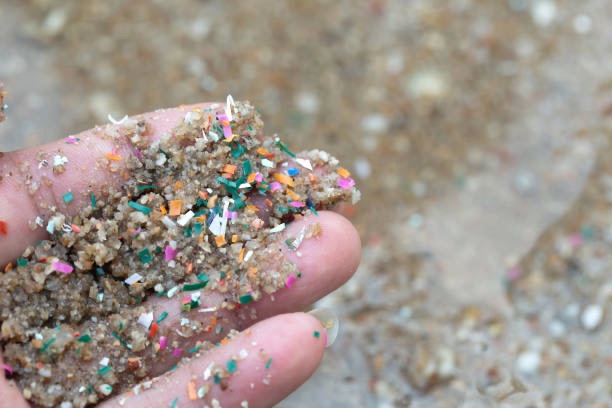
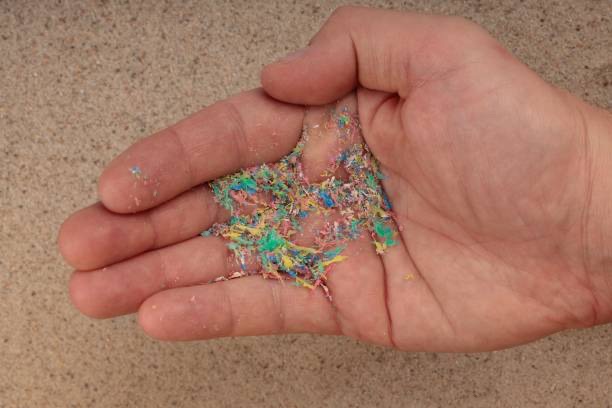
1. Microplastics are small plastic particles, less than 5mm in size, while nanoplastics are extremely small, less than 100 nanometers, and are found in the whole environment, everywhere, in the air, water, and soil. The greatest impact of these small particles on aquatic life has been a trending topic in recent times. The potential hazard to human lives is a great concern, too. Microplastics come from many sources. Tiny particles produced from polyethene plastic are used in many cosmetic products, even in health products, as an exfoliate. Plastic pollution is seen in both food and drink product packaging, the most hazardous being the bottled water. The direct effects of plastic particles, especially chemicals like BPA, on human health are still the subject of ongoing research widely carried out.


2. Microplastics have been used in many industrial and cosmetic products as microbeads. They are also used in toothpaste, as vectors for drug delivery, cleaning agents, plastic packaging in food and drinks, and manufacturing products. Some examples of primary and secondary uses of microplastics:
• Personal care /cosmetics like toothpaste, facial scrubs, and cleansers.
• Agricultural products are used as coatings in fertilisers and in seeds.
Industrial products such as paints, textiles, tyre materials, and many types of machinery.
• Sports like synthetic turf.
• Secondary microplastics are released from packaging and fragmentation of bottles, bags and debris, produced by fragmentation and weathering due to exposure to UV lights, weather and mechanical activity.

3. Microplastics as a global threat has become an issue of grave concern because of their impact on all compartments of the environment, that is, air, water and soil. The most common concern is the food packaging on major food items such as mineral water, drinks, dairy, snacks, meat, fish, and frozen products. The contact of contamination is between the food item and the container/ the outer package is actually the cause of mutual transfer between the content and the plastic. Besides these, microplastics are also found in sediments in freshwater, the ocean, soil ecosystems, and on beaches, becoming a threat to not just humans but also other life on earth, including aquatic animals.
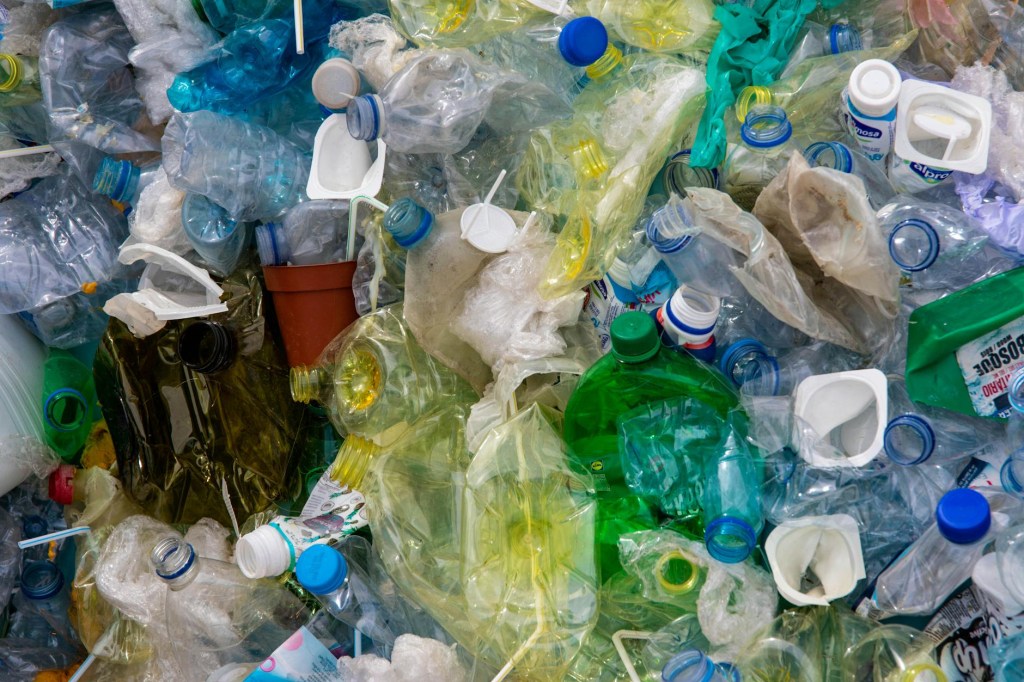

4. Microplastic pollution: Over the years, the growing presence of microplastics in the environment has increased day by day. The microplastics have high polymer content, so they remain non-perishable, non-degradable in soil, and insoluble in water. The direct impact on humans can be:
•Consumption of bottled water and plastic packaged drinks.
•Food packaging of different items.
•Indirect effect of microplastics from consuming aquatic foods like seafood, fish, and crustaceans.
•Personal care items like fabrics ( sportswear), toothpaste, face scrubs, and exfoliating products through micro beads.
•Industrial products.
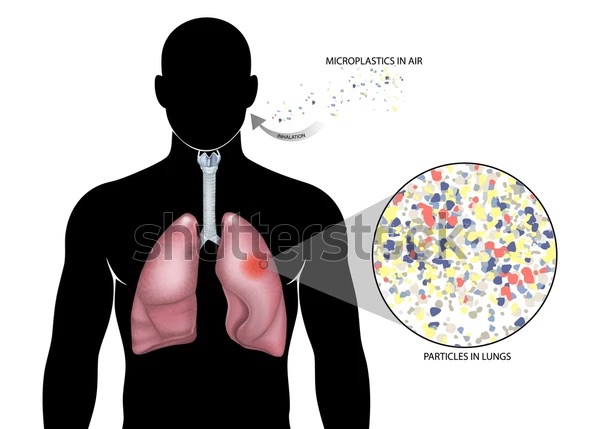
5. Accumulation in the human body: Microplastics/ Nanoplastics easily accumulate in the human body through different sources :
• Ingestion through the food supply chain.
• Inhaled through air pollution.
• Ingested through drinks and water.
• Microplastics can enter the human body through dermal contact via sweat, wounds, an indirect route like unfiltered sewage plant, seawater, and seafood.
6. Recent studies have detected microplastics/nanoplastics in different human tissues and organs, including the brain. Traces are found in blood, liver, kidneys, lungs, and saliva. They mainly enter into different organs and tissues through the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Nanoplastics, which are even smaller ( less than 1micrometer ), are more dangerous as they can infiltrate the human cells. Microplastics have also been found in human breast milk, placenta, meconium, and an infant’s first stool.

7. Impact on human health:
•Oxidative damage: Microplastics can cause oxidative damage, DNA damage and changes ingene activity.
• Reproductive effects can be ovarian scarring, low sperm count, and metabolic disorders in offspring.
• Deposits of BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals can cause damage to the brain, nervous system, reproductive, gastrointestinal and respiratory systems.
• Other effects can be inflammation, cell death, changes in hormone and lipid metabolism, and an altered gut microbiome.
8. Research shows that potential health risks due to absorption, inhalation and ingestion of microplastics and nanoplastics are an alarming public health issue. The most important key effects can be:
• Regular or frequent exposures can cause chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal system, endocrine disruptions, and a weakened immune system.
• Accumulation in the respiratory system can cause lung inflammation, chronic asthma, chronic obstructive lung diseases and lowered lung function.
• The reproductive system can be affected, leading to low sperm count and infertility.
• Accumulation in organs like the liver, kidneys, spleen, and placenta can lead to scarring and functional irregularities.
• Increased risk of cancers and cardiovascular issues.


9. Supporting the body’s natural detoxification process can be useful in removing microplastics to some extent. Some of the proven ways by which microplastics can be removed from the body are:
• Drinking plenty of water helps flush out toxins.
• Sweating it out by physical exercise, running, or walking.
• Consumption of gut-healthy food like fermented food, prebiotics and probiotics.
• Antioxidant-rich foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, berries, and cruciferous vegetables.
• High fibre vegetables for forming bulk and binding the waste to be disposed of from the body.


10. The use of plastic is a global environmental hazard which has been taken seriously worldwide. Some important steps taken are:
• Minimal use of plastics in food supply chains and industrial uses.
• Use of plastic alternatives like bamboo, wood, seaweed, metal, and glass packaging.
• Replacing household items like/with silicon food bags, ceramic, glass utensils, stainless steel containers, wooden utensils.
• Using reusable materials derived from sugarcane, wheat, seaweed, packaging materials like cardboard, paper, plant-based wraps, and foams.
• Natural fibres like jute, organic cotton, and wool.
• Extensive research for the environmental clean-up of plastics and recycling plastics is ongoing in many countries. Plastic-eating bacteria (Ideonella sakaiensis), microbes like Pseudomonas, and Bacillus have been identified which have biodegradable capacity to break down plastics.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏
















