1.Sarcopenia is a musculoskeletal condition mostly common in the elderly population where there is progressive loss of muscle mass. However, today, it can also be linked to certain chronic conditions and lifestyle habits, where the process of muscle loss starts much earlier, even in younger populations, between 30 and 40 years old. Sarcopenia impacts on inability to perform regular daily activities, frequent falls, fractures, reduces quality of life, ageing progression and risks of more complications related to death.
2.The rate of muscle loss increases with advancing age. People with chronic diseases are more prone to sarcopenia than an otherwise normal healthy individual. The process of muscle loss is often noticeable with ageing, but it can be slowed by implementing lifestyle changes. Sarcopenia can affect quality of life as:
• Disability.
• Loss of independence.
• More visits to hospitals.
• Expensive, as increase health care costs, or very likely, a need of institutionalized care can arise.
• Risk of surgical complication.
• Lower rates of survival.

3.As ageing progresses, the muscles of the body lose mass as the body doesn’t produce enough protein. Ageing also brings out hormonal changes like lower levels of testosterone and insulin growth factor, which can further contribute to sarcopenia. There are many risk factors of sarcopenia such as:
• Inadequate protein intake or malnutrition.
• Reduce protein conversion as age advances.
• Lower levels of growth hormones, testosterone, insulin-like-growth factor.
• Increase inflammation.
• Diabetes, insulin resistence.
• Chronic kidney and liver diseases.
• Obesity.
• Cancer, HIV
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
• Rhematoid arthritis, lupus, osteoporosis.
• Congestive heart failure.

4.Important lifestyle factors, including environmental risk factors, can contribute to the early onset and progression of sarcopenia:
• Sedantery lifestyle, lack of exercise.
• Bedridden, bedrest.
• Loss of mobility due to paralysis, neurological causes.
• Improper diet.
• Dental and oral problems.
5. Sarcopenia greatly affects the quality of life. Common symptoms can be :
• Shrinking muscles, muscle atrophy.
• Muscle weakness.
• Inability to perform daily activities.
• Difficulty walking, climibing stairs.
• Loss of stamina and loss of balance.
• Frequent falls, fractures.
• Poor posture, hunched or stooped.

6.Sarcopenia is diagnosed by medical history, visible signs of muscle loss and a series of physical tests and examinations.
• Physical tests like walking speed assessment, grip strength test, chair stand test. SARC-F screening tests.
• Blood tests like hormonal levels, vitamin D levels, markers of inflammation.
• Imaging tests like Xray Absorbptiometry, Bio impedence analysis (BIA).
7.Consultation with a Physician is important when there are visible signs of muscle loss, fatigue and difficulty performing routine physical activity. Consider visiting a Specialist when you have signs:
• Walking slowly, feeling fatique while walking.
• Difficulty getting up from chair, climb stairs, lift heavy objects.
• Loss of balance, frequent falls.
• Thinning of arms and legs.
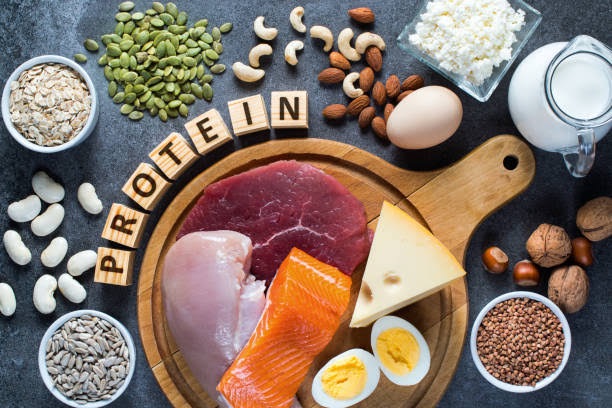


8. Usually, bringing about lifestyle changes and improving diet can make a great difference in improving or bringing positive changes in Sarcopenia patients. Potential treatments of Sarcopenia can be:
• Treating the underlying conditions.
• Exercise routine as per individual requirements like resistence training, aerobic exercises.
• Nutritional interventions, like increasing protein intake like meat, fish, eggs, soy protein. Nutritional supplements like vitamin D, Omega 3 fatty acid and creatine.

9.There are ways which can slow down the process of muscle loss and maintain muscle mass as age advances:
• As ageing progresses, the body’s ability to synthesise and break down protein reduces, which is known as anabolic resistance. So, the protein intake should be increased to 1-1.3/kg of body weight daily.
• Most important is maintaining an active lifestyle with regular exercise of walking, resistance training to maintain lean muscle mass.
• Regular sleep pattern.
• Nutritional supplements like Vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and creatine are essential.

10.Last but not the least, the process of ageing and muscle loss are inevitable with time, but making changes in lifestyle habits and diets can bring about positive changes and delay the process. Studies have greatly shown that the quality of life and lifespan can be improved by effective ways of improving diet with high-quality protein, strength and resistance training, walking daily, reducing stress and adequate sleep.
Thanks for reading.
Peace and love 🙏